Agentic commerce at scale: Why startups are key in building robust AI-powered shopping experiences

Online shopping is now so ubiquitous that it is hard to remember a time when the only way to buy a hat or pair of jeans was at an actual store.
Lost in the seemingly “quick” transition from brick-and-mortar storefront to your mobile phone was the work it took to build today’s infrastructure, where online shopping now accounts for 20% of all retail sales worldwide. Even though the necessary technology was available to make a rapid transition, it still took startups and incumbents time to build reliable payment, fraud detection and delivery systems that now support more than $6 trillion in global online shopping revenue.
A similar dynamic is unfolding with agentic commerce, albeit on a much faster – and more compressed – time scale. Thanks to Generative AI (Gen AI), the total addressable market for agentic commerce is slated to hit $1.7 trillion by 2030, a CAGR of 67% from the $136 market value in 2025.
However, the transition to agentic commerce, like the switch to ecommerce, relies on more than just the underlying technology. Agentic commerce requires an entirely new infrastructure for transactions from start-to-finish. As part of this transition, companies will need to innovate and create new business models, not only to support different types of shopping journeys but also to monetize them. In addition, incumbents and startups will have to tackle issues related to authentication, fraud detection and know your agent (KYA), which need to be addressed to scale any meaningful agentic commerce efforts.
Collaboration is, and will continue to be, essential for agentic commerce to be successful. Traditional efforts, with incumbents innovating in partnerships with startups, will be crucial, but so will non-traditional tie ups between incumbents who usually compete for business. This is already playing out, with new announcements related to agentic commerce coming out on what seems like a daily basis.
As with other emerging spaces, being first is key. From launching products to building payment and identity rails, companies and startups that want to shape the future of agentic commerce are already making waves.
Why Agentic Commerce?
Consumers are shifting how they find products and make purchases at a rapid pace, with more than one in four Americans saying they have used an AI tool instead of a traditional search engine. Nearly 40% of shoppers have used Gen AI for purchases, a 1300% year-over-year increase that has led major retailers to view the technology as a strategic differentiator that enhances customer engagement on websites.
AI agents will ultimately provide a simpler shopping journey, eliminating the need for shoppers to toggle between websites and wonder which one offers the best deal. By aggregating information from across multiple sources, agents will be able to:
- Shrink the product search and comparison journey into a single natural language query
- Provide personalized recommendations based on pricing preferences, product features, user reviews and shipping details
- Optimize checkout by using stored credentials and applying all available discounts
Immediate Effects on Retailers
A simpler shopping journey for consumers, however, does not translate into an easier, or even linear, process for merchants. Many of the tools and strategies they have relied on for years, such as search engine optimization (SEO) and email marketing, will have to be re-calibrated to stay vibrant in an agentic commerce paradigm.
This will play out across four areas for retailers:
- Product discovery: As consumers shift away from search engines, retailers will see declines in organic traffic, as well as traffic from investments in SEO. Ultimately, customer acquisition costs will increase as retailers fight to have their product recognized by an AI platform.
- Product curation: Traditional marketing funnels, where a lead is taken through a specific path and converts through a product purchase, will break down as AI platforms interrupt current linear journeys.
- strong>Checkout: Retailers will have to invest money in agentic checkout processes, specifically “know your agent” (KYA) protocols that mitigate for theft and fraud. These efforts will require additional investments that retailers may or may not have already earmarked.
- strong>Post-Purchase: Agents, not individuals, making purchases means retailers will have less direct access to consumer data. That could affect how they follow up with customers and make post-purchase marketing funnels less effective.
How Are Payments Evolving in the Age of Agentic Commerce?
Major players are already launching products and forging partnerships to have the most influence on how the world of agentic commerce takes shape.
In the near term, we expect the payment rails currently governing ecommerce to persist, but the process of payment method selection could change rapidly. Shoppers may choose their payment method on a per-purchase basis or by saving credentials with their “agent of choice” to be used for all purchases. Agents could also choose a payment method optimized for earning rewards or even self-select alternative or proprietary methods like buy now pay later (BNPL). It is likely that different ecosystem participants will have unique or proprietary agents (LLM agents, search/browser/social agents, merchant/marketplace agents, category-specific agents), so effective cooperation with these agents will be key to payment method provider success.
From an infrastructure perspective, incumbents are already leveraging startup expertise to enable AI agents:
- Visa’s “Intelligent Commerce” initiative will facilitate secure transactions between AI agents and consumers, using tokens, APIs and customizable spending controls to create personalized and trustworthy transactions.
- Mastercard’s “Agent Pay” service will help consumers make secure purchases within conversational AI platforms using tokens. Agents will determine payment methods based on context and user preferences.
- PayPal launched its “Agent Toolkit” to help developers incorporate the company’s suite of APIs into agentic commerce workflows.
- Stripe’s agent toolkit allows developers to integrate its payment offerings into agentic frameworks, helping agents spend funds and support related operations.
Startups have been crucial in current efforts to fully realize the potential of AI agents, and incumbents will continue to rely on new and emerging entrants in the agentic commerce space to power future iterations.
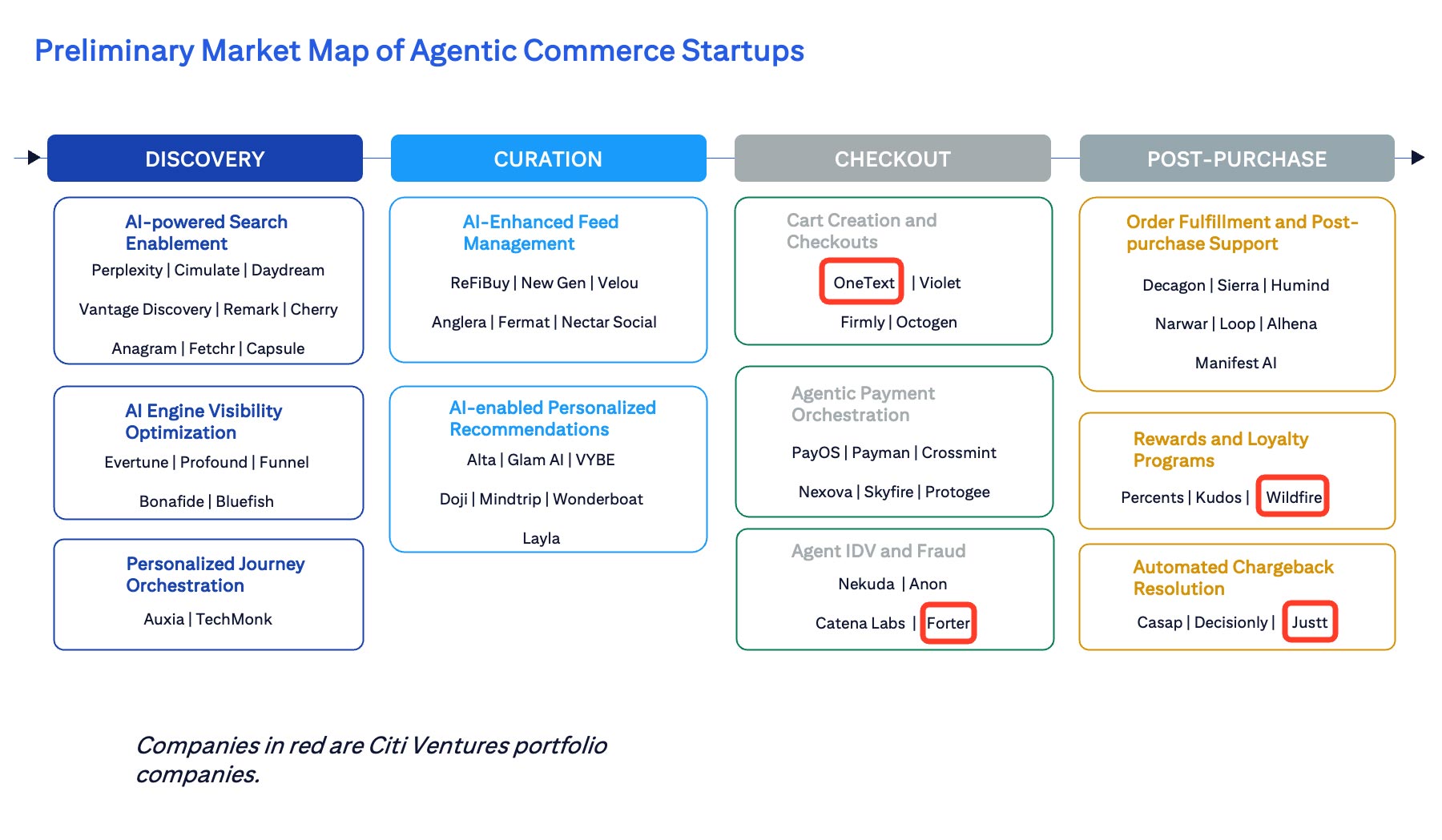
Emerging Startups and Technology
Startups with innovative business models are addressing specific pain points across the evolving agentic customer journey. These include:
- Auxia’s Agentic Marketing Platform helps businesses deploy AI agents that automate data analysis, determine actions and personalize content, enhancing customer engagement and driving revenue growth.
- Crossmint specializes in providing API infrastructure that enables enterprises to integrate digital wallets and crypto payments for retail and agentic commerce.
- Justt automates the end-to-end process of fighting fraudulent or invalid chargebacks for merchants.
- Onetext offers a conversational commerce platform that enables merchants to allow their users to complete transactions by directly responding to their text message marketing messages.
- PayOS delivers an advanced card-native payment solution that enables AI agents to autonomously manage and execute real-world financial transactions for businesses and individuals.
- Profound helps brands understand how AI crawlers access and interpret their content, orient for AI-driven search and take advantage of ways to become more visible.
- Velou provides an AI-powered product catalog that empowers AI agents to autonomously manage and deliver high-resolution product data.
- Wildfire Systems powers rewards programs and shopping companions, which will be key as companies look to hook in consumers post-purchase.
What’s Next
Agentic commerce is still taking shape, and companies and startups have a lot of work to do to build up the infrastructure necessary to take it beyond simple hype. As with the shift from physical stores to ecommerce, the ultimate transition will take time and not be immediate.
Issues such as consumer habits and loyalty to legacy solutions will have to be overcome, as will concerns about trust and fraud. In addition, companies and startups will have to continually adapt to emerging regulatory schemes that will arise, affecting what business models take shape and how they operate.
However, the flurry of recent product announcements and partnerships demonstrate the momentum behind agentic commerce. Startups will be key in unlocking the technology’s potential, and they will help incumbents build a new infrastructure that makes ecommerce more personalized and efficient.